UPDATE:
The on-premise version of Mailsac has been ended. Contact support@team.mailsac.com to learn more about our dedicated instances instead, or visit mailsac.com/enterprise.
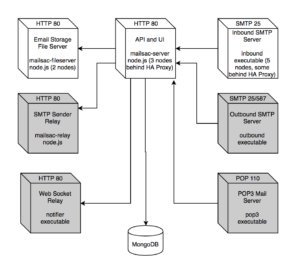
On-Premise Mailsac now comes with the Dockerfiles and docker-compose.yml to get up and running in seconds using Docker.
Each Mailsac microservice can be run independently with Docker. A convenient Makefile is included alongside the Dockerfile in each service, with a sample task for running in docker (make docker-run).
Frontend API+UI example:
$ cd frontend
$ make docker-run
docker build -t mailsac/frontend .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 4.34MB
Step 1/7 : FROM node:8-alpine
---> 406f227b21f5
Step 2/7 : RUN apk update && apk add git
---> Using cache
---> d4e543b7bbe6
Step 3/7 : COPY . /opt/frontend
---> c23657034aba
Step 4/7 : WORKDIR /opt/frontend
Removing intermediate container 776dfd90f8e7
---> 5558d5ac56ab
Step 5/7 : RUN npm i --production
---> Running in 3b4298ca4ae0
added 333 packages in 12.184s
Removing intermediate container 3b4298ca4ae0
---> 8adfac5691b0
Step 6/7 : EXPOSE 3000
---> Running in 3070214927bd
Removing intermediate container 3070214927bd
---> 199808362a19
Step 7/7 : CMD node app.js
---> Running in e5ceede43634
Removing intermediate container e5ceede43634
---> 3dafbb6f3f2e
Successfully built 3dafbb6f3f2e
Successfully tagged mailsac/frontend:latest
docker run --rm -d -p 0.0.0.0:3000:3000 --name=mailsac mailsac/frontend
9533f06a0751e1a7ebb67de93b563e14679fed634d567728d81681fc99d6211d
docker logs -f frontend
------ Mailsac ------
connecting to mongo
started message disk cache
connected to mongo
Inbound SMTP server:
$ make docker-run
go build -ldflags '-s -w -X main.gitversion=v15.0.1'
docker build --no-cache -t mailsac/inbound .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 4.619MB
Step 1/5 : FROM alpine
---> 3fd9065eaf02
Step 2/5 : COPY inbound /opt/inbound
---> 1d14457a75fc
Step 3/5 : WORKDIR /opt
Removing intermediate container a97ae6ac27e0
---> a4230e86d399
Step 4/5 : EXPOSE 25 587
---> Running in e43b166f773e
Removing intermediate container e43b166f773e
---> 4bdc6745ff78
Step 5/5 : ENTRYPOINT ["/opt/inbound"]
---> Running in b812c4442101
Removing intermediate container b812c4442101
---> 620d169d15f1
Successfully built 620d169d15f1
Successfully tagged mailsac/inbound:latest
docker run --rm -d -p 0.0.0.0:25:25 -p 0.0.0.0:587:587 --name=inbound mailsac/inbound
cef23b5af410f0f5663727ad1c16cda5d070d3232ad2d5ee94db5b64562ad513
docker logs -f inbound
syslog connected:127.0.0.1:514
Starting server on port 587
Starting server on port 25
A sample docker-compose.yml file is also included. As a result you can have a fully running set of Mailsac services without even deploying it, in seconds. It should serve as a good starting point for understanding how the services talk to each other, and setting up your own deployment using pure Docker, Docker + Ansible, or an orchestrator like Kubernetes.
$ docker-compose up --build
Building relay
Step 1/7 : FROM node:8-alpine
---> 406f227b21f5
Step 2/7 : RUN apk update && apk add git
---> Using cache
---> d4e543b7bbe6
Step 3/7 : COPY . /opt/relay
---> Using cache
---> bdd144f2089f
Step 4/7 : WORKDIR /opt/relay
---> Using cache
---> 58a37f36a693
Step 5/7 : RUN npm i --production
---> Using cache
---> c0be4245ebf6
Step 6/7 : EXPOSE 3007
---> Using cache
---> 88c4d2f6c6b9
Step 7/7 : CMD node server.js
---> Using cache
---> f5b8551d0fbd
Successfully built f5b8551d0fbd
Successfully tagged ms2_relay:latest
Building notifier
Step 1/4 : FROM alpine
---> 3fd9065eaf02
Step 2/4 : COPY notifier /opt/notifier
---> Using cache
---> 5ee53ef401f3
Step 3/4 : EXPOSE 8080
---> Using cache
---> 57fb8f8fe110
Step 4/4 : ENTRYPOINT /opt/notifier
---> Using cache
---> 35ac15e5cc01
Successfully built 35ac15e5cc01
Successfully tagged ms2_notifier:latest
Building frontend
Step 1/7 : FROM node:8-alpine
---> 406f227b21f5
Step 2/7 : RUN apk update && apk add git
---> Using cache
---> d4e543b7bbe6
Step 3/7 : COPY . /opt/frontend
---> 37b9ad50d96f
Step 4/7 : WORKDIR /opt/frontend
Removing intermediate container a2b4b26dbac3
---> 0d1c573b307b
Step 5/7 : RUN npm i --production
---> Running in 535408d85bd6
npm WARN deprecated mimelib@0.3.1: This project is unmaintained
npm notice created a lockfile as package-lock.json. You should commit this file.
added 333 packages in 11.041s
Removing intermediate container 535408d85bd6
---> 95016c15e489
Step 6/7 : EXPOSE 3000
---> Running in 4879a888ecea
Removing intermediate container 4879a888ecea
---> a086e8e90f50
Step 7/7 : CMD node app.js
---> Running in 834c6bc77297
Removing intermediate container 834c6bc77297
---> 3a815540ed78
Successfully built 3a815540ed78
Successfully tagged ms2_frontend:latest
Building outbound
Step 1/5 : FROM alpine
---> 3fd9065eaf02
Step 2/5 : COPY outbound /opt/outbound
---> Using cache
---> 76eba650e12d
Step 3/5 : EXPOSE 587
---> Using cache
---> 15e317117cf7
Step 4/5 : WORKDIR /opt
---> Using cache
---> 8e337b87460e
Step 5/5 : ENTRYPOINT ["/opt/outbound"]
---> Using cache
---> 755c189ce229
Successfully built 755c189ce229
Successfully tagged ms2_outbound:latest
Building pop3
Step 1/4 : FROM alpine
---> 3fd9065eaf02
Step 2/4 : COPY pop3 /opt/pop3
---> Using cache
---> 23743111b4ae
Step 3/4 : EXPOSE 9090 110
---> Using cache
---> 757d6120f3c3
Step 4/4 : ENTRYPOINT /opt/pop3
---> Using cache
---> 4f9969d09d90
Successfully built 4f9969d09d90
Successfully tagged ms2_pop3:latest
Building inbound
Step 1/5 : FROM alpine
---> 3fd9065eaf02
Step 2/5 : COPY inbound /opt/inbound
---> fbf61d35f8af
Step 3/5 : WORKDIR /opt
Removing intermediate container 7ed35fdd8d8a
---> dbf3f6c46c4d
Step 4/5 : EXPOSE 25 587
---> Running in 0ffeb91b767e
Removing intermediate container 0ffeb91b767e
---> dffa069abe07
Step 5/5 : ENTRYPOINT ["/opt/inbound"]
---> Running in f1cf5e565847
Removing intermediate container f1cf5e565847
---> 841f16e95ee1
Successfully built 841f16e95ee1
Successfully tagged ms2_inbound:latest
Building filer
Step 1/4 : FROM alpine
---> 3fd9065eaf02
Step 2/4 : COPY filer /opt/filer
---> Using cache
---> a700eb91ac4d
Step 3/4 : EXPOSE 3005
---> Using cache
---> 8e2c5401bf0a
Step 4/4 : ENTRYPOINT /opt/filer
---> Using cache
---> 1b578459a892
Successfully built 1b578459a892
Successfully tagged ms2_filer:latest
Starting ms2_mongo_1 ...
Starting ms2_mongo_1 ... done
Starting ms2_notifier_1 ... done
Recreating ms2_frontend_1 ... done
Recreating ms2_inbound_1 ...
Recreating ms2_filer_1 ...
Recreating ms2_pop3_1 ...
Recreating ms2_inbound_1 ... done
Attaching to ms2_relay_1, ms2_mongo_1, ms2_notifier_1, ms2_frontend_1, ms2_filer_1, ms2_pop3_1, ms2_outbound_1, ms2_inbound_1
relay_1 | starting app server on port 3007
notifier_1 |
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.328+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] MongoDB starting : pid=1 port=27017 dbpath=/data/db 64-bit host=d2b548e5f949
notifier_1 | ---- Mailsac Notifier Startup ----
notifier_1 |
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.328+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] db version v3.6.2
relay_1 | verifyKeys failed Skipping default domain DKIM verificiation due to missing private key file
notifier_1 | Connecting to db at mongo:27017
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.328+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] git version: 489d177dbd0f0420a8ca04d39fd78d0a2c539420
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.329+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] OpenSSL version: LibreSSL 2.6.3
frontend_1 | No YAML parser loaded. Suggest adding js-yaml dependency to your package.json file.
relay_1 | mailsac relay server listening on port 3007
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.329+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] allocator: system
filer_1 | syslog connected:127.0.0.1:514
pop3_1 | syslog connected: 127.0.0.1:514
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.330+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] modules: none
filer_1 |
filer_1 | ---- Mailsac Filer Startup ----
filer_1 |
outbound_1 | syslog connected:127.0.0.1:514
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.330+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] build environment:
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.330+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] distarch: x86_64
pop3_1 | ---- Mailsac POP3 Server and HTTP Server Startup 0.0.0.0 ----
pop3_1 | mailsac base api is http://frontend:3000
pop3_1 | Started pop3 server on port 1100
inbound_1 | syslog connected:127.0.0.1:514
pop3_1 | starting metrics listening at 0.0.0.0:9090/metrics
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.330+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] target_arch: x86_64
filer_1 | Starting up server 0.0.0.0:3005 using TLS=%!b(bool=false)
outbound_1 | ---- Starting Mailsac Outbound SMTP Server 0.0.0.0:587 ----
inbound_1 | Starting server on port 587
filer_1 | will register availability as filer:3005
pop3_1 | 2018/03/11 23:20:16 Server listening on: 0.0.0.0:1100
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.331+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] options: { net: { bindIp: "0.0.0.0" } }
inbound_1 | Starting server on port 25
filer_1 | base data folder is /data/mailsac
filer_1 | cleanup start folder=/data/mailsac
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.337+0000 I - [initandlisten] Detected data files in /data/db created by the 'wiredTiger' storage engine, so setting the active storage engine to 'wiredTiger'.
filer_1 | cleanup found folder empty - done
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:13.351+0000 I STORAGE [initandlisten] wiredtiger_open config: create,cache_size=487M,session_max=20000,eviction=(threads_min=4,threads_max=4),config_base=false,statistics=(fast),log=(enabled=true,archive=true,path=journal,compressor=snappy),file_manager=(close_idle_time=100000),statistics_log=(wait=0),verbose=(recovery_progress),
filer_1 | failed constructing registration!! http://frontend:3000/api/fileserver-registration/filer%3A3005 Get http://frontend:3000/api/fileserver-registration/filer%3A3005: dial tcp 172.18.0.5:3000: connect: connection refused
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:14.427+0000 I STORAGE [initandlisten] WiredTiger message [1520810414:427265][1:0x7fbefc2d9730], txn-recover: Main recovery loop: starting at 17/5248
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:15.204+0000 I STORAGE [initandlisten] WiredTiger message [1520810415:204706][1:0x7fbefc2d9730], txn-recover: Recovering log 17 through 18
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.173+0000 I STORAGE [initandlisten] WiredTiger message [1520810416:172793][1:0x7fbefc2d9730], txn-recover: Recovering log 18 through 18
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.480+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.481+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Access control is not enabled for the database.
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.481+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted.
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.481+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.567+0000 I FTDC [initandlisten] Initializing full-time diagnostic data capture with directory '/data/db/diagnostic.data'
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:16.568+0000 I NETWORK [initandlisten] waiting for connections on port 27017
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.005+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.4:50314 #1 (1 connection now open)
notifier_1 | Connected to db
notifier_1 | Starting up server 0.0.0.0:8080 using TLS= false
frontend_1 |
frontend_1 | ------ Mailsac ------
frontend_1 |
frontend_1 | connecting to mongo
frontend_1 | started message disk cache
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.398+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.5:37510 #2 (2 connections now open)
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.399+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.5:37512 #3 (3 connections now open)
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.407+0000 I NETWORK [conn2] received client metadata from 172.18.0.5:37510 conn: { driver: { name: "nodejs", version: "2.2.35" }, os: { type: "Linux", name: "linux", architecture: "x64", version: "4.9.60-linuxkit-aufs" }, platform: "Node.js v8.9.4, LE, mongodb-core: 2.1.19" }
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.408+0000 I NETWORK [conn3] received client metadata from 172.18.0.5:37512 conn: { driver: { name: "nodejs", version: "2.2.35" }, os: { type: "Linux", name: "linux", architecture: "x64", version: "4.9.60-linuxkit-aufs" }, platform: "Node.js v8.9.4, LE, mongodb-core: 2.1.19" }
frontend_1 | connected to mongo
frontend_1 | starting app server on port 3000
frontend_1 | server listening 3000
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.444+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.5:37514 #4 (4 connections now open)
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.449+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.5:37516 #5 (5 connections now open)
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.452+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.5:37518 #6 (6 connections now open)
mongo_1 | 2018-03-11T23:20:17.455+0000 I NETWORK [listener] connection accepted from 172.18.0.5:37520 #7 (7 connections now open)
The original Ansible based server deployment scripts are still included. After a few requests for Docker, it was decided to make it easier for prem customers to run themselves. Both Docker and non-Docker Ansible deployments will be supported for the foreseeable future.